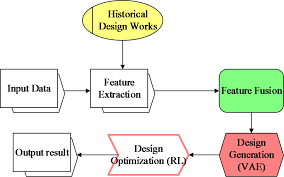
This study proposes a novel artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted design model that combines Variational Autoencoders (VAE) with reinforcement learning (RL) to enhance innovation and efficiency in cultural and creative product design. By introducing AI-driven decision support, the model streamlines the design workflow and significantly improves design quality. The study establishes a comprehensive framework and applies the model to four distinct design tasks, with extensive experiments validating its performance. Key factors, including creativity, cultural adaptability, and practical application, are evaluated through structured surveys and expert feedback. The results reveal that the VAE + RL model surpasses alternative approaches across multiple criteria. Highlights include a user satisfaction rate of 95%, a Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) score of 0.92, model accuracy of 93%, and a loss reduction to 0.07. These findings confirm the model’s superiority in generating high-quality designs and achieving high user satisfaction. Additionally, the model exhibits strong generalization capabilities and operational efficiency, offering valuable insights and data support for future advancements in cultural product design technology.
Research background and motivations
Globally, the cultural and creative industries are becoming increasingly significant drivers of economic growth1,2,3. This industry spans not only traditional arts and design fields but also includes diverse sectors such as advertising, media, software, and gaming4,5,6. Existing design practices predominantly depend on the experience and intuition of designers. While effective for certain straightforward creative tasks, these approaches exhibit considerable limitations when confronted with complex cultural and creative design challenges. For instance, traditional design processes often involve lengthy timelines, requiring repeated manual creation and modification, which hinders quick adaptation to market demands. Designers frequently face constraints imposed by their existing experience and styles, impeding their ability to overcome innovation barriers. Complex design tasks typically demand substantial time and human resources, posing a significant burden for small to medium-sized creative teams. With the rapid development of digital technology, particularly the widespread application of artificial intelligence (AI), the field of cultural and creative product design is facing unprecedented opportunities for transformation7,8. AI technology, by providing new tools and methods, brings unique perspectives and endless possibilities to creative design9,10,11. The introduction of AI models offers a promising solution to these issues by automating the generation of design solutions, optimizing decision-making processes, and enhancing both design efficiency and creativity. This shift can significantly reduce resource consumption and alleviate the constraints faced by traditional design methods.
However, despite AI’s innovative momentum in the creative industries, it also poses a series of challenges and issues12,13,14. Designers often face difficulties in adopting and integrating these new technologies, including concerns about the potential impact of technological dependence on creativity and originality. Moreover, the fusion of AI with creative thinking requires deeper understanding and research15,16,17. Additionally, the adaptability and cultural sensitivity of AI technology are areas of concern, as cultural products must not only meet market demands but also convey the values and significance of specific cultures.
This study focuses on the application of Variational Autoencoders (VAE) and reinforcement learning (RL) in the design field. These AI technologies have demonstrated strong capabilities in pattern recognition, data generation, and decision optimization. However, their potential in cultural and creative product design remains underexplored. By investigating how VAE and RL can support the creative process, this study seeks to enhance design innovation and responsiveness to market trends while evaluating the impact of AI on designers’ creative autonomy.
Research objectives
The main objectives of this study are as follows: (1) to analyze and evaluate the application and potential of AI technologies, specifically VAE and RL, in cultural and creative product design; (2) to construct an interdisciplinary framework that integrates theory and practice, aiming to deepen the understanding of the role of AI technologies in the design process and their impact on creative output; (3) to explore how designers adopt and accept these technologies and their specific influences on design practice; and (4) to empirically assess the effectiveness of AI-assisted design tools in enhancing design innovation, efficiency, and market adaptability. The study focuses on a diverse selection of cultural artifacts, including textiles, ceramics, furniture, and digital art products. This range spans from traditional craftsmanship to contemporary design, enabling a thorough evaluation of AI technologies’ applicability and performance across different types of cultural and creative product design. By encompassing these domains, the study provides a comprehensive assessment of how AI technologies can be integrated into various design contexts.
Application of AI in creative design
In recent years, AI technology has made substantial advancements in the field of creative design. Researchers have explored various AI methods, including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), VAEs, and RL, to drive innovation in design processes.
For instance, Hosseini and Rajabipoor Meybodi21 proposed a comprehensive model for the sustainable development of Iran’s creative industries, leveraging digital transformation and explanatory structural modeling. Mateja and Heinzl22 analyzed existing computational cultural creative systems based on machine learning, offering practical guidance for designing such systems in diverse contexts. As et al.23 introduced a graph-based machine learning system capable of handling three-dimensional structures. This approach extracted significant components as subgraphs and recombined them into new cultural product designs, demonstrating a structured and compositional methodology beyond conventional media like images or text. Mahmud et al.24 explored cultural creative product studies within human-AI collaborative environments, emphasizing the potential for human-AI symbiosis as a future direction for AI integration in cultural industries. Xie25 examined the appearance, decorative elements, and compositional features of intangible cultural heritage products, employing shape grammar to extract and transform heritage elements into preliminary design concepts. Fiebrink26 presented teaching strategies grounded in educational research and creative computing practices to support students in achieving their goals in creative computing.
These technological advancements not only improve the efficiency of design processes but also facilitate the generation of novel ideas. For instance, AI can quickly generate design options, provide inspiration, and address complex design challenges. Research has shown how AI can analyze market trends and consumer preferences to propose design solutions tailored to market needs. Additionally, AI has demonstrated remarkable potential in artistic creation, enabling artists to produce innovative works that redefine traditional art forms and contribute to their evolution.