Background: While portable devices capable of single-lead ECG acquisition have the potential to enhance the scale of structural heart disease (SHD) screening, noise during the acquisition of portable ECGs decreases the performance of deep learning models. Here, we developed and multi-nationally validated a noise-adapted artificial intelligence (AI) model to detect the presence of SHD from single-lead ECGs.
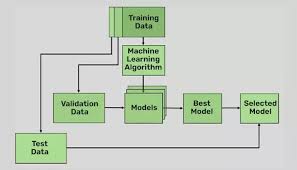
Methods: We developed ADAPT-HEART (AI Deep learning for Adapting Portable Technology in HEART disease detection) using lead I ECGs paired with echocardiograms within 30 days from 110,228 patients at Yale New Haven Hospital during 2015-2023. We validated the model in five community hospitals and practices in the Northeastern US (N=65,988), and the population-based cohort of the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil) (N=3,014). SHD was defined by the presence of LVEF <40%, moderate or severe left-sided valvular disease, or severe LVH (IVSd >15 mm + moderate or severe LV diastolic dysfunction). We developed label-specific convolutional neural networks (CNN) using ECG signals augmented with random Gaussian noise to make models resilient to noisy ECG acquisition. The CNN output probabilities and the patient’s age and sex were ensembled using extreme gradient boosting to detect SHD.
Results: In the development set, 32% had SHD compared with 31-56% across the community hospital sources and 3% in ELSA-Brasil. ADAPT-HEART achieved an AUROC of 0.88 (95% CI, 0.87-0.89) for detecting SHD. With optimized Youden’s index, the model has a sensitivity of 86%, specificity of 82%, PPV of 54%, and NPV of 96% for detecting SHD in the held-out test set. The model performed consistently across US data sources (AUROC: 0.81-0.89) and ELSA-Brasil (AUROC: 0.86) with comparable performance across key demographic subgroups. The model showed better discrimination in detecting a composite SHD that encompasses severe valvular disease, rather than moderate or severe valvular disease (AUROC, 0.91).
Conclusion: ADAPT-HEART, a noise-adapted AI model for 1-lead ECGs, is able to detect a composite of several treatable SHDs with consistent performance across multinational data sources. By integrating outputs from a growing number of wearable/portable devices with ECG capabilities, ADAPT-HEART can enable low-cost, large-scale screening for SHDs in the community.