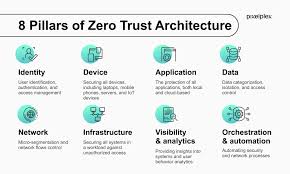
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, zero-trust architecture has emerged as a critical framework for protecting digital assets and sensitive information. As organizations struggle with increasingly sophisticated cyber threats and stringent data protection regulations, integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into zero-trust models has become a game changer.
As distributed networks expand, endpoints are becoming increasingly critical within zero-trust architectures, requiring stronger security controls. AI is being integrated into zero-trust architectures to enhance security enforcement and threat detection, making access controls more dynamic. Let’s examine the challenges and opportunities at this complex intersection of technology and regulation.
AI Makes Zero Trust Intelligent
The integration of AI into zero-trust frameworks represents a significant evolution in cybersecurity strategies. AI enhances zero-trust models by providing advanced threat detection, response and decision-making capabilities. This leads to a stronger overall security posture of organizations. One key area where AI is making a substantial impact is continuous authentication and authorization.
AI-powered continuous authentication and authorization are integral to modern zero-trust architecture. These systems utilize AI to analyze user behavior, device security posture and network conditions in real time, thereby making context-aware access decisions. By leveraging AI, organizations can implement dynamic authentication processes that go beyond traditional methods. For instance, AI can monitor user behavior patterns and flag any deviations from normal activity, triggering additional verification steps when necessary. This approach ensures that access permissions are continuously verified and updated.
The role of AI in enhancing contextual access decisions within zero-trust frameworks cannot be overstated. AI excels at processing and analyzing vast amounts of data in real time, allowing for sophisticated risk assessments for each access request. For example, a user tries to access a system from an unrecognized device or unusual location. In that case, AI can flag this as a higher-risk scenario and prompt additional authentication steps. This capability enables organizations to implement adaptive access policies that adjust based on real-time risk evaluations that are also appropriate to the current context.
Beyond authentication, AI-driven analytics can also proactively detect insider threats, automate security responses and improve network segmentation within a zero-trust framework.
Hurdles Of Legacy Systems
Integrating AI into zero-trust models comes with its challenges, particularly those pertaining to legacy systems. Many organizations are still using outdated infrastructure that was not designed with zero-trust principles in mind. Implementing zero trust in these legacy systems while leveraging AI and meeting regulatory requirements presents significant challenges. The security protocols and capabilities that are required to seamlessly align with the zero-trust model are often missing in legacy systems, making integration complex, costly and at times impossible. Organizations may need to upgrade or replace outdated technology, which involves identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities and ensuring compatibility with zero-trust principles.
Moreover, the interoperability issues between legacy systems and modern zero-trust solutions can be substantial. Legacy systems often operate on outdated protocols and technologies that may not be compatible with AI-driven security measures, requiring the use of middleware or other bridging technologies to facilitate communication between old and new systems. This complexity is further compounded by the need to ensure that all systems, including legacy infrastructure, comply with modern data protection laws and regulations.
Navigating The Regulatory Landscape
As organizations implement zero-trust architectures, they must also wade through the complex landscape of data protection regulations. Laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States have set high standards for data privacy and security. These regulations require organizations to implement stringent security measures, including zero-trust principles, to protect personally identifiable information (PII) and ensure compliance.
One of the key challenges in this regulatory landscape is ensuring that zero-trust architectures comply with data residency and cross-border data transfer restrictions. Many countries have laws that require certain types of data to be stored and processed within their borders, complicating the implementation of global IT strategies. These data localization requirements can act as non-tariff barriers, making it more expensive and time-consuming to transfer data internationally.
Working With The Challenges
To address these challenges, organizations must carefully design their zero-trust architectures to comply with data localization and cross-border data transfer restrictions while maintaining the security and efficiency of their models. This may involve implementing sophisticated data handling and storage protocols that align with regulatory standards, potentially requiring the use of hybrid cloud models that use both local data centers and cloud services that comply with specific regional regulations.
By leveraging AI for advanced data classification and access control, organizations can more effectively manage data in accordance with various regulatory frameworks. AI-powered systems can analyze data in real time, determining its sensitivity and applying appropriate access controls based on the user’s location, role and other contextual factors. This capability is especially valuable when dealing with cross-border data transfers, as AI can help data compliance with relevant regulations as it moves across different jurisdictions.
AI’s ability to process and analyze data in real time allows for swift detection of potential threats, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers. By accurately distinguishing between benign irregularities and genuine threats, AI has the potential to reduce false positives and allows security teams to focus on real threats.
As AI continues to advance and data protection laws evolve, the zero-trust model will continue to adapt, offering new opportunities to strengthen cybersecurity. Ongoing investment, innovation and a balanced approach to security needs with regulatory compliance and user privacy will be required for successful implementation.